This blog aims to inform you about the different causes of knee pain, the treatment options available, and when to seek professional help, so that you are equipped with the knowledge to manage your condition effectively.
Written by

Angel Rigueras
Pain Management Specialist
Share
Written by

Angel Rigueras
Pain Management Specialist
Follow
Table of content
Related content
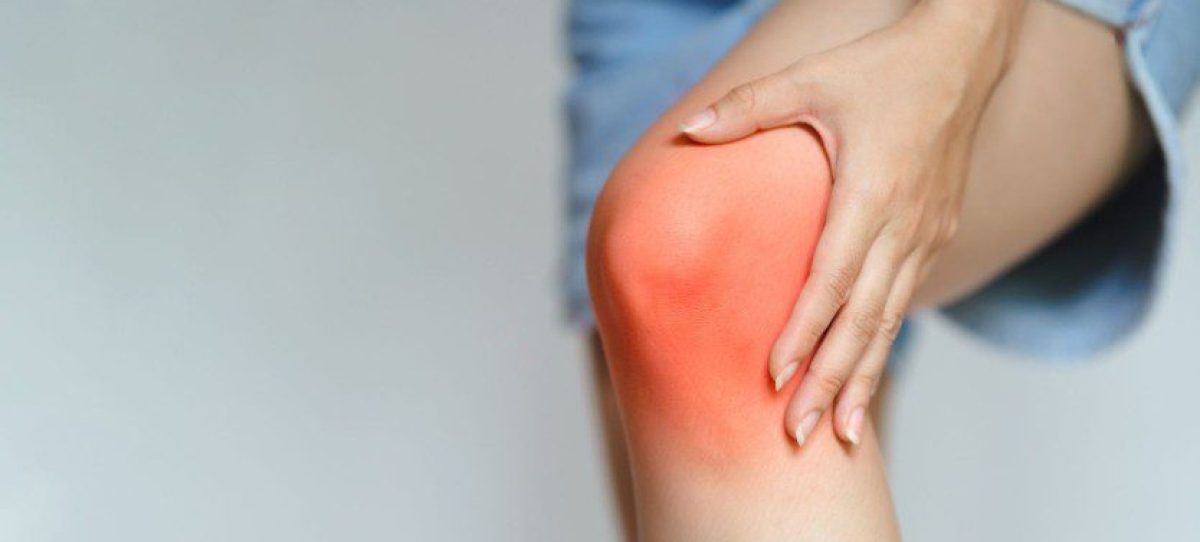
Knee pain is a common complaint that affects millions of Americans each year, resulting in more than 6 million doctor visits annually (about 2.5% of the US population). Knee pain can result from a spectrum of issues ranging from acute injuries to ongoing conditions resulting from stress and wear.
The knee connects the upper and lower leg bones, playing a crucial role in various movements such as walking and running. It allows bending, straightening, and slight rotation of the leg, being the largest joint in the body.
The knee joint is made up of three bones with specific roles in joint movement, stability, and force transmission:
The articular cartilage covers the joint surfaces, facilitating smooth movement and providing nutrition via synovial fluid. It plays a significant role in reducing friction during knee movements.
The Meniscus are C-shaped pieces of cartilage that help distribute body weight, stabilize the knee, and allow for a limited range of motion during twisting movements. They are susceptible to injury, particularly during rapid motion.
The knee joint is supported by four primary ligaments—two collateral (medial and lateral) and two cruciate (anterior and posterior)—which provide stability and restrict excessive movement in different directions.
The knee’s motion is enabled by various muscles and tendons, primarily the quadriceps and hamstrings. These muscles are responsible for extending and bending the knee, respectively.
Knee pain is a common musculoskeletal symptom among working-age people. The prevalence of knee pain varies from 10 to 60%. The most prevalent knee injuries involve soft tissue tears (ligaments and meniscus), often affecting multiple structures. Let’s take a look at some of the most common knee injuries:
ACL injuries frequently occur in sports involving cutting and pivoting, such as soccer, football, and basketball. Rapid changes in direction or improper landings can lead to ACL tears, which often accompany damage to other knee structures like articular cartilage and menisci.
PCL injuries often result from a blow to the front of the bent knee, commonly seen in motor vehicle accidents or contact sports. These injuries are usually partial tears that may heal on their own.
Collateral ligament injuries typically arise from forces pushing the knee sideways, often due to contact. MCL injuries often result from direct blows to the knee’s outer side, while blows to the inner side may injure the LCL, which occurs less frequently.
Acute meniscal tears often occur with injuries, including sports injuries through twisting or cutting movements or tackling.
Quadriceps and patellar tendon injuries can happen to anyone but are more common in middle-aged individuals involved in running or jumping sports. Other common causes include falls, direct impacts to the knee, and awkward landings.
The patella is the most commonly fractured bone around the knee, alongside the femur and tibia at their joint. Many fractures in this area result from high-energy trauma, such as falls and vehicle accidents.
Dislocations occur when the knee bones are misaligned, either partially or completely. This can involve the femur and tibia or the patella. Dislocations may stem from structural abnormalities or result from high-energy trauma such as falls, vehicle accidents, or sports injuries.
Knee pain is a common issue, and several factors can contribute to its development. Here are some key risk factors to be aware of:
While some knee sounds, like clicking or grinding, are typically harmless, pain paired with these noises should prompt a visit to a specialist. The location and severity of knee pain may vary, depending on the cause of the problem. Signs and symptoms that sometimes accompany knee pain include:
Paying attention to the severity and type of symptoms is essential, as more intense or multiple symptoms may signal a more serious underlying problem.
At UOC, we believe in a patient-centered approach to treat your condition. Depending on the cause and severity of your knee pain, we offer a range of treatment options designed to relieve discomfort, restore function and improve your quality of life.
It is estimated that only 20 percent of individuals with knee pain require surgery.
Our objective is to provide our patients with an efficient and effective solution to alleviate their discomfort, facilitating a timely return to their daily activities with minimal disruption. Our team of specialists is equipped to perform minimally invasive techniques to facilitate a swift recovery.
When non-surgical options do not provide sufficient relief, our experienced orthopedic surgeons may recommend surgical interventions. Options include:
Preventing knee pain is possible through simple lifestyle adjustments. Our specialists emphasize the importance of engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding repetitive stress on the knees.
Here are some strategies for healthier knees:
Knee pain is a prevalent issue, often caused by injuries or long-term wear and tear.
Understanding the knee’s anatomy and common causes of pain, such as ligament tears, fractures, and joint morphological changes, is essential in recognizing symptoms and seeking proper treatment.
By staying active, maintaining a healthy weight via physicial conditioning, and practicing proper techniques, you can prevent knee injuries and maintain joint health.
Don’t let knee pain hold you back from living your best life. Consult with a healthcare provider to explore your options and take the first step toward healthier, pain-free knees!
To learn more about our knee pain treatments or to schedule a consultation, call us today at (866) 961-1744 or fill out our convenient online appointment request form. We look forward to serving you!
Related content
